Huzhou
Huzhou
湖州市 Huchow | |
|---|---|
Left to right, top to bottom: the twin towers of Soochow International Plaza viewed from Xiangwang Park, the Huancheng River at night, skyline seen from Renhuang Mountain with the Huzhou Olympic Stadium visible, the Sheraton Huzhou Hot Spring Resort, Yishang Street, and Laohutan Reservoir south of the city | |
 | |
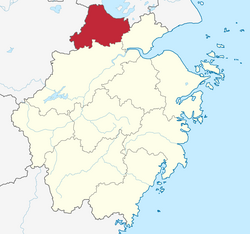 Location of Huzhou City jurisdiction in Zhejiang | |
| Coordinates (Huzhou municipal government): 30°53′33″N 120°05′15″E / 30.8925°N 120.0875°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Zhejiang |
| County-level divisions | 5 |
| Township-level divisions | 66 |
| Municipal seat | Wuxing District |
| Government | |
| • CPC Secretary | Ma Xiaohui (马晓辉) |
| • Mayor | Qian Sanxiong (钱三雄) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 5,818.43 km2 (2,246.51 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,566.8 km2 (604.9 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 860.42 km2 (332.21 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 census) | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 3,367,579 |
| • Density | 580/km2 (1,500/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,558,826 |
| • Urban density | 990/km2 (2,600/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,015,937 |
| • Metro density | 1,200/km2 (3,100/sq mi) |
| GDP[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | CN¥ 320 billion US$ 41.1 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 95,579 US$ 13,646 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Area code | 0572 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-ZJ-05 |
| License Plate | 浙E |
| Languages | Huzhou dialect |
| Website | www |
| Huzhou | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 湖州 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wu | ghou² cieu¹ (Huzhounese) wu⁶ tseu¹ (Shanghainese) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Capital of the Lake District | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Huzhou (Chinese: 湖州; pinyin: Húzhōu, ; Huzhou dialect: ghou² cieu¹) is a prefecture-level city in northern Zhejiang province (Hangzhou–Jiaxing–Huzhou Plain, China). Lying south of the Lake Tai, it borders Jiaxing to the east, Hangzhou to the south, and the provinces of Anhui and Jiangsu to the west and north respectively. As of the 2020 census, its population was 3,367,579 inhabitants, of whom 1,015,937 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of Wuxing District as Nanxun District is not being conurbated yet.
Location
[edit]Huzhou, in its general aspect, is in the center of the Yangtze River Delta Economic Area, with the city center 10 km (6.2 mi) south of the Chinese third largest freshwater lake Lake Tai. There are transportation links to the provincial capital of Hangzhou 78 km (48 mi) away in the south, Jiangsu and Anhui province in the west, and the metropolitan municipality of Shanghai 150 km (93 mi) to the northeast.
Flowing quietly through the city is the Changxing-Huzhou-Shanghai Channel, it is also referred to as the "Eastern Rhine River" for the continuous barge transportation that goes on similarly in the more internationally known Rhine River in Germany.
The State Way 318 passes through Huzhou in an east–west direction and the State Way 104 in a north–south direction; the Nanjing-Huzhou-Hangzhou toll expressway and Shanghai-Jiangsu-Zhejiang-Anhui toll expressway offers convenient access to major areas in the region.
The Express Xuancheng–Hangzhou Railway Station is located 8 km (5.0 mi) west of the city center. This railway line is part of the "secondary tunnel" in eastern China.
History
[edit]
- 248 BC, Gucheng County (菰城縣) was set up by the State of Chu.
- 222 BC, Qin dynasty, Wucheng County (烏程縣) was set up.
- 266, Kingdom of Wu, set Wuxing Shire (吳興郡), its administrative area including the modern Huzhou prefecture city and Hangzhou, Yixing in modern-day Jiangsu.
- 602, Sui dynasty, changed the name of Wuxing to Huzhou (湖州).
- During the Tang dynasty, Huzhou administered 5 counties: Wucheng (烏程), Wukang (武康), Changxing, Anji, and Deqing.
- At the beginning of the Song dynasty, Gui'an county (歸安縣) was divided from the Wucheng county.
- During the Qing dynasty, Huzhou administered 7 counties: Wucheng, Guo'an, Wukang, Deqing, Changxing, Anji, and Xiaofeng.
- 1949, with the establishment of the People's Republic of China, Huzhou town became the seat of government of the First Special District of Zhejiang, administrative area including the modern Huzhou and Jiaxing prefecture cities.
- 1983, Huzhou prefecture level city was set up.
Climate
[edit]Huzhou has a typical subtropical monsoon climate in Jiangsu South. Summers are hot, winters are mild, and there are four distinct seasons with abundant rainfall. The average annual temperature is 16.3 degrees Celsius and the total annual precipitation is 1303.4 mm.
| Climate data for Huzhou (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 23.0 (73.4) |
28.0 (82.4) |
32.4 (90.3) |
33.5 (92.3) |
36.4 (97.5) |
37.5 (99.5) |
39.2 (102.6) |
40.9 (105.6) |
37.7 (99.9) |
33.4 (92.1) |
27.8 (82.0) |
24.8 (76.6) |
40.9 (105.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 7.7 (45.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
15.0 (59.0) |
21.2 (70.2) |
26.1 (79.0) |
28.7 (83.7) |
33.0 (91.4) |
32.4 (90.3) |
27.9 (82.2) |
22.8 (73.0) |
17.0 (62.6) |
10.5 (50.9) |
21.1 (69.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.0 (39.2) |
6.2 (43.2) |
10.5 (50.9) |
16.3 (61.3) |
21.5 (70.7) |
24.8 (76.6) |
28.8 (83.8) |
28.3 (82.9) |
24.1 (75.4) |
18.4 (65.1) |
12.4 (54.3) |
6.3 (43.3) |
16.8 (62.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.2 (34.2) |
3.1 (37.6) |
6.9 (44.4) |
12.3 (54.1) |
17.6 (63.7) |
21.7 (71.1) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.3 (77.5) |
21.1 (70.0) |
15.0 (59.0) |
8.9 (48.0) |
3.0 (37.4) |
13.5 (56.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.0 (17.6) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
2.0 (35.6) |
8.6 (47.5) |
13.8 (56.8) |
18.5 (65.3) |
18.9 (66.0) |
12.1 (53.8) |
4.0 (39.2) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 88.2 (3.47) |
79.1 (3.11) |
109.7 (4.32) |
91.9 (3.62) |
115.1 (4.53) |
223.9 (8.81) |
162.2 (6.39) |
169.9 (6.69) |
97.4 (3.83) |
77.6 (3.06) |
65.2 (2.57) |
56.0 (2.20) |
1,336.2 (52.6) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 12.1 | 11.0 | 13.9 | 12.5 | 12.6 | 15.4 | 12.9 | 13.9 | 10.6 | 8.2 | 10.1 | 8.9 | 142.1 |
| Average snowy days | 3.7 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 8.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 77 | 76 | 74 | 72 | 73 | 80 | 78 | 79 | 79 | 78 | 78 | 76 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 110.3 | 110.5 | 136.3 | 159.5 | 169.1 | 126.3 | 202.6 | 194.5 | 154.2 | 158.8 | 131.7 | 128.1 | 1,781.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 34 | 35 | 36 | 41 | 40 | 30 | 47 | 48 | 42 | 45 | 42 | 41 | 40 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[2][3]all-time extreme temperature[4] | |||||||||||||
Population
[edit]According to the seventh census data, as of midnight on November 1, 2020, the city's permanent population was 336,7579.[5]
At the end of 2011, Huzhou had a registered population of 2,611,700, of which 1,31,700 were men and 1,38,800 were women; 851,700 were non-farmers, up 22,700 from the previous year; and 511,200 were over 60. For the whole year, the birth rate was 7.96 per thousand, the death rate was 6.79 per thousand, the natural growth rate was 1.17 per thousand and the family planning rate was 98.08 per cent.
According to the sixth national census in 2010, the city's resident population stood at 2893,542,[6] an increase of 267,753 or 10.20 percent over the fifth national census, with an average annual growth rate of 0.98 percent. Of these, the male population was 1470,472, or 50.82 per cent, and the female population was 1423,070, or 49.18 per cent. The sex ratio of the total population (100 females) is 103.33.The population aged 0–14 years is 337,688, or 11.67 per cent; the population aged 15–59 years is 2086,891, or 72.12 per cent; and the population aged 60 years and over is 468,963, or 16.21 per cent; of the population aged 65 years and over is 3150,37 or 10.89 per cent. The population living in urban areas is 1530,418, or 52.89 per cent, and the population living in rural areas is 1,363,124, or 47.11 per cent.
Administration
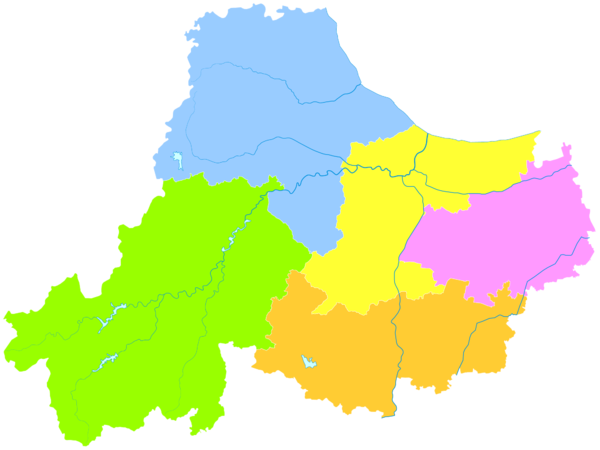
[edit]The prefecture-level city of Huzhou administers six county-level divisions, including one economic development zone and two districts and three counties.
These are further divided into 66 township-level divisions, including 50 towns, 10 townships and six subdistricts.
| Map | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subdivision | Hanzi | Pinyin | Population (2020) | Area (km2) | Density | |
| City Proper | ||||||
| Wuxing District | 吴兴区 | Wúxīng Qū | 1,015,937 | 871 | 869.30 | |
| Suburban | ||||||
| Nanxun District | 南浔区 | Nánxún Qū | 542,889 | 716 | 748.67 | |
| Rural | ||||||
| Changxing County | 长兴县 | Chángxīng Xiàn | 673,736 | 1,388 | 462.52 | |
| Deqing County | 德清县 | Déqīng Xiàn | 548,568 | 936 | 525.41 | |
| Anji County | 安吉县 | Ānjí Xiàn | 486,409 | 1,882 | 247.90 | |
- Huzhou Economic Development Zone (湖州经济开发区)
Economy
[edit]- Huzhou is known as the City of Silk, is one of the Four Capital-cities of Silk in China.
- Textiles (especially silk), building materials and agriculture.
- In 2022, Huzhou will achieve a regional gross domestic product of 385.0 billion yuan, an increase of 3.3 percent over the previous year. The value-added structure of tertiary industries was 4.2:51.1:44.7.The per capita GDP of the resident population was 112,902, an increase of 2.7 per cent.
- Huzhou is one of the 14 key cities in the Yangtze River Delta region, which has been opened to the outside world for development and development. In 2019, Huzhou's gross domestic product (GDP) stood at 312.24 billion yuan, up 7.9% from the previous year at comparable prices, exceeding the province's target of 8% set at the beginning of the year. Of this total, the value-added of primary industries rose 2.8 percent to 13.38 billion yuan, the value-added of secondary industries rose 7.6 percent to 159.54 billion yuan, and the value-added of tertiary industries rose 8.7 percent to 139.32 billion yuan. The value-added structure of tertiary industries was 4.3:51.1:44.6 and the proportion of tertiary industries was 0.8 percentage points higher than the previous year. GDP per capita is 102,593 yuan, or 14,900 dollars.
- Total fiscal revenue was 17.235 billion yuan, of which local revenue was 9.727 billion yuan, up 17.5 percent and 21.6 percent respectively over the previous year. Total fiscal revenue as a share of GDP is 13.2%.
Military
[edit]Huzhou is headquarters of the 1st Group Army of the People's Liberation Army, one of the three group armies that comprise the Nanjing Military Region responsible for the defense of China's eastern coast.
Public Spaces
[edit]- Lotuses Garden

The Lotus Garden (pinyin "Lianhua Zhuang") is a pleasure garden located 20 minutes south on foot from the city center of Huzhou. The main attractions of the garden include the Lotus flowers that bloom seasonally in the three lake system, a large Koi pond near the north gate, a karaoke veranda and amusement rides for children. Also, barge-themed pedal boats are available for leisure boating.

The garden was built in 1924 with stone footpaths and bridges bordering and crossing over the lake system. A variety of structures inhabit the 300 meter squared grounds including two halls, six pavilions, and two inlets, all following the harmonious design of traditional Chinese architecture. Sign posts describe local history and the halls maintain a Tea House where visitors may converse and take a break from the rays of the sun. A particular geological feature worth seeing are the ancient stones transferred from Lake Tai. Families pour into the garden on public vacation days while local people partake in tai chi exercise, or play card and Mahjong games every day, year round. The garden is open during daytime hours and admission is free of charge.
- Xiangwang Park
Xiangwang Park (Southwest Gate Park) is a more recent addition to Huzhou's collection of historical parks. It was built in 2009 and located at Chen Bei Bridge. The park includes the rebuilt wooden gate outpost on top of the original defensive wall. A visitor ship is permanently moored one kilometer west of the historic gate.
- Long Island Park
Long Island Park (pinyin "Changdao Gongyuan") is a new park just north of the city center on an island stretching north–south in the middle of Xitiao River. It was built in 2009. The park is open every day. A popular destination for local residents after dinner, the lengthy route becomes something of a promenade for people taking their daily constitutional through the form of a jog or, more commonly, a walk. There is a small golf park, a historical pool, and a garden available to visitors.
Transportation
[edit]Huzhou is served by Huzhou railway station, situated to the west of the city. Both conventional and high-speed trains stop at the station.
Travel
[edit]Huzhou has unique scenery, the style of small bridges and flowing water in the east, and the charm of mountain meadows in the western Chinese bamboo township. It has given birth to six tourism brands: "Taihu Lake, Bamboo Township, Famous Mountain, Wetland, Mansion Gate, and Paleoecology".

Feiying Pagoda in the central urban area has become a national key cultural relic protection unit with a tower within a tower; The Iron Guanyin in the Iron Buddha Temple is famous overseas for the reputation of the Venus of the East. The eight scenery of Wuxing on the outskirts of the city is still beautiful. Nanxun Ancient Town is a famous town in Jiangnan, and there are many scenic spots in the town, such as Jiayetang Library Building, Baijian Building, Zhang Shiming's Former Residence, Xiaolian Zhuang and so on.
Anji, China's bamboo township, Longwang Mountain at the source of the Huangpu River, Tianhuangping Pumped Storage Power Station, a national industrial tourism demonstration point, and the China Bamboo Expo Park, which has the largest area and complete bamboo species in China, seem to be a green corridor in the Yangtze River Delta, accompanied by the pure melody of bamboo music, showing tourists the tourism positioning of "green ecology"; Deqing Moganshan, a national scenic spot in the cool world, is known as China's four major summer resorts together with Lushan, Beidaihe and Jigongshan.
Xiazhu Lake in Deqing is the largest wetland scenic area in Jiangnan, which is a newly developed natural ecological scenic spot; Jiangnan Mansion Gate Nanxun, with the connotation of world cultural heritage, has become a symbol of the ancient town of water town together with the thousand-year-old town of Deqing.
Located at the junction of Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Anhui provinces, Changxing has become a witness of paleoecology with its ten-mile ancient ginkgo corridor, "living fossil" Yangzi crocodile, golden nails from the second glacial period site and Tang dynasty tribute tea purple shoot tea.
International relations
[edit]Twin towns—Sister cities
[edit]Huzhou is twinned with:
 Radom, Poland[7]
Radom, Poland[7] Kalmar County, Sweden
Kalmar County, Sweden Cabo Frio, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil[8]
Cabo Frio, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil[8]
Notable people
[edit]- Zhu Zhi (朱治; 156–224) and Zhu Ran (朱然; 182–248), military general for the Kingdom of Wu during the Three Kingdoms era of China.
- Shen Yue (沈約; 441–513), prominent scholar of the Liang dynasty and author of the Book of Song.
- Chen Baxian (陳霸先; 503–559), founder and Emperor Wu of Chen dynasty during Northern and southern dynasties era.
- Lu Yu (陸羽; 733–804), sage of tea, author of the Classic of Tea.
- Zhao Mengfu (趙孟頫; 1254–1322), great calligrapher and high officer in Yuan dynasty.
- Guan Daogao (1262 - 1319?), calligrapher and author.
- Yu Yue (俞樾; 1821–1906), scholar.
- Shen Jiaben (沈家本; 1840–1913), Late Qing Chinese scholar and jurist.
- Wu Changshuo (吳昌碩; 1844–1927), great calligrapher.
- Chen Qimei (陳其美; 1878–1916), revolutionary, member of Chinese Tongmenghui. Chen Guofu (陳果夫) and Chen Lifu (陳立夫) are nephews of Chen Qimei.
- Lei Zhen (雷震; 1897–1979), politician and political analyst of the Republic of China.
- Dai Jitao (戴季陶; 1891–1949), politician of the Republic of China.
- Zhu Jiahua (朱家驊; 1893–1963), politician of the Republic of China.
- Zhao Jiuzhang (赵九章; 1907–1968), (ancestral roots in Wuxing) meteorologist and physicist.
- Qian Sanqiang (錢三强; 1913–1992), scientist in Chinese atomic bomb study; and his father Qian Xuantong (錢玄同; 1887–1939), scholar.
- Tu Shou'e (屠守鍔; 1917–2012), scientist and rocket designer.
Specialty
[edit]- Silk:
Huzhou is well known as one of the birthplaces for silk cultivation. In 1958, a great number of silk, silk ribbon and uncarbonized tablets were found in the southern suburbs of Huzhou. Scientists from the Institute of Archaeology measured these silk products carefully and determined the age of the silk to date back 4700 years. Now, these silk pieces have become the greatest treasures of the Zhejiang Silk Museum. Huzhou silk has many desirable features, such as paleness in color, luster, flexibility, and roundness in shape. As a result, Huzhou silk has been respected and desired for a very long time. The history of Huzhou silk can be uncovered back to the time of the Warring States (474 BC –221 BC). By the time of the Southern and Northern Dynasties (420 AD – 589 AD), Huzhou silk had already been exported to more than ten countries. During the Tang dynasty (618 AD – 907 AD), Huzhou silk was chosen for an imperial tribute, thus marking the first prosperity in silk production. With the establishment of the Ming dynasty (1368 AD – 1644 AD), the residents living near Lake Tai entered the profitable textile industry, resulting in a larger workforce and a refinement of Huzhou silk products. Huzhou silk has won awards at World Fairs, and is desired by clothing and furnishing manufacturers overseas.[9][better source needed]
- ""Huzhou ink brush""
Huzhou has a long history of manufacturing ink brushes, and it can be traced back to the Qin dynasty. Huzhou's ink brush production and manufacture gained prominence in the Ming dynasty (13th century). Since the late 20th century, Huzhou has been known as the "Hometown of the Ink Brush". Huzhou also holds an annual "Huzhou Ink Brush Festival", and the festival also has some memorial activities dedicated to Meng Tian - the inventor of ink brush pen. The most famous brush pen workshop in Huzhou could be the Shanlian (善琏; Shàn Liǎn), thus its brush pens are named Shanlian Hubi (善琏湖笔; Shànliǎn Húbǐ) in reverence of this workshop. Shanlian is also a local place name, whose ancient name was Mengxi (Chinese: 蒙溪; lit. 'creek of Meng Tian'). Meng Tian made brush pens there.
- Zhou Shenji's Wonton

The now popular Huzhou style Wonton dish is known to be introduced by an ingenious man named Zhouji. It is said that in 1930, Mr. Zhouji saw how profitable Ding Lianfang's roadside restaurant (began in 1878) was by serving a noodle bowl with bean curd dumplings. As a result of this observation, Zhouji also opened a store to compete for the same clients. Soon after, Mr. Zhouji found that his roadside restaurant could not replicate his competitors profit and was forced to close. However, considering what his competitor did not sell, he rethought his plans. He opened a new roadside restaurant called "Zhou Shengji's". Unlike his first venture, this one made a profit. He sold a wonton bowl with flower dumplings filled with various ingredients. The dumplings could have pork, with your choice of mix such as celery, bamboo, or spinach. And Zhou Shenji's cooks continue to be very particular about the quality of dumpling they serve. They select all the raw materials very carefully, such as wheat flower, sesame, sesame oil, wine, sugar, salt and other spices that need to be added to create the flower dumpling shell. Furthermore, Zhouji invented a special process so that dumplings do not break up easily when boiled. Combined with a special sauce, the dumplings have a satisfying taste and thus are a very popular dish.[citation needed]
See also
[edit]
References
[edit]- ^ 浙江省统计局. "2021年浙江统计年鉴 17-2 各市国民经济主要指标(2021年)" (in Chinese (China)). Archived from the original on 2020-08-17. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 25 June 2023.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 25 June 2023.
- ^ 【浙江高温可能破纪录】今天最新预报,杭州报8月4日42℃,绍兴报8月3-4日43℃,如果实现都将打破当地观测史最高气温纪录。图3简单列举了部分浙江城市的观测史最高气温纪录。 (in Simplified Chinese). weatherman_信欣 on Weibo. Retrieved 22 September 2024.
- ^ "3367579人!湖州市第七次全国人口普查主要数据公布-腾讯新闻". view.inews.qq.com. Retrieved 2023-06-21.
- ^ 湖州市统计局. 《湖州市2010年第六次全国人口普查主要数据公报》.
- ^ "Radom - Miasta partnerskie" [Radom - Partnership cities]. Miasto Radom [City of Radom] (in Polish). Archived from the original on 2013-04-03. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- ^ "Cabo Frio e Huzhou, na China, fecham acordo e se tornam cidades irmãs" [Cabo Frio and Huzhou in China close deal and become sister cities] (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2018-05-05.
- ^ "huzhou silk history." baidu. baidu, 09 May 2009. Web. 30 Oct 2013. <http://zhidao.baidu.com/link?url=CM4uZMECsupncKVKYyTqYMeoFtCAK1AfMw2LwhBsCKTexNGe2thEvG89mxTFhm2bq-xYtNUKF_L0F36GXI-t_q>.
External links
[edit]- Government website of Huzhou (in Chinese)
- . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.